RRD (Route
Redistribution) allows different routing protocols to
exchange routing information.
RRD (Route
Redistribution) allows different routing protocols to
exchange routing information. Using a routing protocol to advertise
routes that are learnt by other means, such as another routing protocol, static
routes, or directly connected routes, is called redistribution.
While running a single routing protocol throughout an entire IP
internetwork is desirable, multi-protocol routing is widespread
for a number of reasons (e.g. company mergers, multiple departments
managed by multiple network administrators, and multi-vendor environments).
If a single routing protocol cannot be used, RRD is the only solution.
Running different routing protocols is often part of a network design.
Every routing protocol on a network is separated into an Autonomous
System (AS). All routers in the same
autonomous system (running the same routing protocol) have complete
knowledge of the entire AS. A router
that connects two (or more) autonomous systems is known as a Border
Router (BR). A BR advertises routing information
from one AS to the other ASs. It is not possible to redistribute
routing information for different routing protocols. Different routing
protocols have different and often incompatible algorithms and metrics.
To access Route Redistribution screens,
go to .
Redistribution BGP Configuration
Figure 1. Redistribution BGP Configuration

| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to configure redistribution
of the routes that are learnt through other routing protocols to BGP. |
Note: To enable BGP functionality,
enable BGP by going to
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Select—click
to select the BGP routes for which RRD status needs to be deleted.
- BGP Status—select the route redistribution
status for BGP. The default option
is Disabled. The list contains:
- Enabled—imports the specified
routes into BGP and distributes the BGP learnt routes to IGP (Interior
Gateway Protocol) (RIP and OSPF). Redistributes route information
for both internal and external BGP..
- Disabled—removes the specified routes from BGP and does not distribute
or import routes from IGP (RIP and OSPF).
- Import Routes—select Import Routes and
control the redistribution of routes. The default option is Direct
Route. The list contains:
- Direct—enables import of directly
connected routes into BGP.
- Static—enables import of static routes into BGP.
- RIP—enables import of RIP routes into BGP.
- OSPF—enables import of OSPF routes into BGP.
- ALL—enables import of all routes into BGP.
- Route Map Name—enter the Routemap Name
that identifies the specified route-map in the list of route-maps.
This value is a string of maximum size 20.
- Metric Value—enter the Metric Value that
needs to be applied to the route before it is advertised into the
BGP. This value is the domain Metric used for generating the default
route. If the metric value is not specified, the default metric
value considered as 1. The value used is specific to the protocol.
This value ranges from 1 and 2147483647.
- Match Type—select the metric type applied
to the route before it is advertised into the OSPF domain. The options
are:
- External—redistributes OSPF external routes
- Internal—redistributes OSPF internal routes
- NSSA-External—redistributes OSPF NSSA external routes
Note: This
field is enabled only when the Import Routes are set as OSPF Routes.
|
| Buttons |
- ADD—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|
Redistribution RIP Configuration
Figure 2. Redistribution RIP Configuration
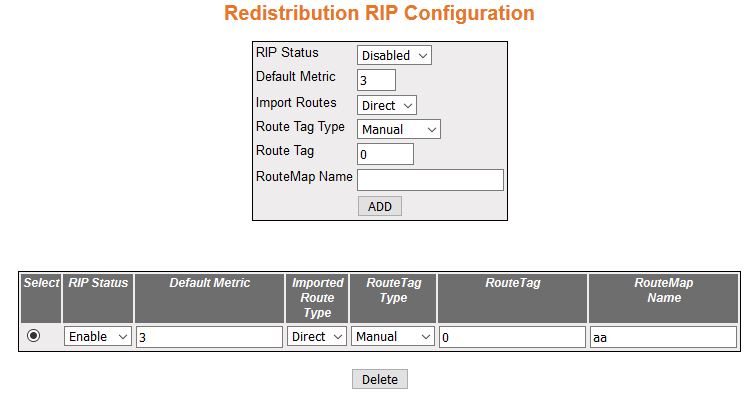
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to configure redistribution
of the routes that are learnt through other routing protocols to RIP. |
Note: To enable RRD RIP status,
create VRF instance by using
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Select—click
to select the RIP routes for which RRD status needs to be deleted.
- RIP Status—select the route redistribution
status for RIP. The default option is Disabled. The list contains:
- Enabled—sets the route redistribution status as enabled. When
enabled, it advertises the routes learned by other protocols and
redistributes route information for both internal and external RIP.
- Disabled—sets the route redistribution status as disabled and
stops redistribution of routes but sends updates to the RTM.
- Default Metric—enter the default metric
for the imported routes. This value ranges from 0 to 16. The default
value is 3.
- Import Routes—select Import Routes to
be imported to RIP. The default
option is Direct. The list contains:
- Direct routes—enables
import of directly connected routes into RIP.
- Static—enables import of static routes into RIP.
- BGP—enables import of BGP routes
into RIP.
- OSPF routes—enables import of OSPF routes
into RIP.
- Route Tag Type—elect whether the tag
is manually configured or automatically generated. The default option
is Manual. The list contains:
- Manual—generates the tags
manually.
- Automatic—generates the tag automatically.
- Route Tag—enter the Route Tag if the
Route Tag type is selected as Manual. This value ranges from 0 to
65535. The default value is 0.
- Route Map Name—enter the name that identifies
the specified route map in the list of route-maps. This value is
a string of maximum size 20.
|
| Buttons |
- ADD—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|
Redistribution OSPF Configuration
Figure 3. Redistribution OSPF Configuration

| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to configure the
redistribution of the routes that are learnt through other routing
protocols to OSPF. |
Note: To enable RRD OSPF status, OSPF must be enabled using
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Select—click
to select the RIP routes for which
RRD status needs to be deleted.
- OSPF Status—select the OSPF Status. The default option
is Disabled. The list contains.
- Enabled—sets the OSPF status as enabled. When enabled
the advertises the routes learnt by other protocols.
- Disabled—stops the redistribution of the routes but updates
the Common Routing Table using the queue interface
- Import Routes / Imported Route Type—select
the source protocols from which routes are imported to OSPF. The default option is Direct
routes. The list contains:
- Direct routes—enables import
of directly connected routes into OSPF.
- Static routes—enables import of static routes into OSPF.
- RIP routes—enables import of RIP routes
into OSPF.
- BGP—enables import of BGP routes
into OSPF.
- ALL—enables import of all routes into OSPF.
- Route Map Name—enter the name that identifies
the specified route-map in the list of route-maps. This value is
a string of maximum size 20.
- Metric Value—sets the Metric Type applied
to the route before it is advertised into the OSPF Domain External link type
associated with the default route advertised into the OSPF routing domain.
- Metric Type—select the Metric type applied
to the route before it is advertised into the OSPF domain. The default option
is Type 2 External. The list contains:
- Type 1 External—sets
metric type as Type 1.
- Type 2 External—sets metric type as Type 2.
|
| Buttons |
- ADD—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|