This section describes how to configure all Syslog-related
parameters.
The Syslog is a standard for
logging program messages. It separates the software that generates
and stores messages from the software that reports and analyze them.
Syslog is a protocol used to capture log information from the
devices on a network. This protocol provides a transport for allowing
a machine to send event notification messages across IP networks
to event message collectors, also known as Syslog servers. This
protocol is simply designed to transport the event messages.
The transmission of syslog messages may be started on a device
without a receiver being configured or even actually physically
present. This simplicity has greatly aided the acceptance and deployment
of syslog.
To access SYSLOG Settings screens, go
to .
In the figure below, click the hyperlink BSD SYSLOG.
BSD stands for Berkeley Software
Distribution (BSD) at University of California where this protocol
has been originally developed.
Figure 1. SYSLOG Settings

BSD Syslog
To access SYSLOG
Settings screens, go to
By
default, the tab Syslog Settings displays
the BSD Syslog Settings Configuration screen.
Figure 2. BSD Syslog Settings
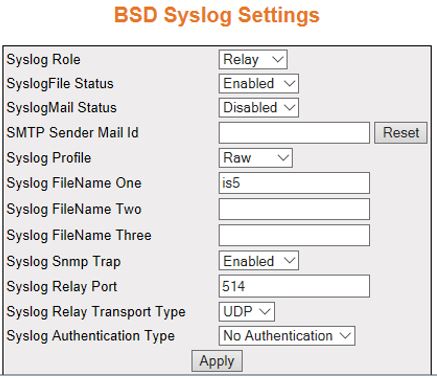
BSD Syslog Settings
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user configure the BSD Syslog settings. |
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Syslog Role—select
Syslog Role. The default option is Device. The list contains:
- Device—sets the syslog role as Device. This generates and forwards
the syslog messages.
- Relay—sets the role as Relay. This receives, generates, and
forwards the syslog messages. It checks if the received packet is
as per BSD Syslog format, and
if it is not, the message is made to BSD Syslog
format and then forwarded.
- SyslogFile Status—select the status of
the syslog storage. When enabled, the syslog messages are stored
in a file (as configured by admin). The default option is Disabled.
The list contains:
- Enabled—enables the syslog local
storage option.
- Disabled—disables the syslog local storage option.
- SyslogMail Status—select the status of
syslog mail storage in the system. Syslog supports sending syslog
message to any mail-id as configured by the admin. The default option
is Disabled.The list contains:
- Enabled—enables the
syslog mail storage option. When enabling syslog mail storage, the
device sends the Syslog messages as mail messages to the mail-server
configured in the system.
- Disabled—disables the syslog mail storage option.
|
| Fields (cont) |
- SMTP Sender Mail Id—enter
the sender mail ID to which email alerts should be sent using SMTP.
The user can customize to add support for specific event for which
email alerts should be sent. This maximum length is 100. The default
value is [email protected].
- Syslog Profile—select the status of the
syslog storage. When enabled, the syslog messages are stored in
a file (as configured by admin). The default option is Disabled.
The list contains
- Raw—sets the syslog profile as Raw which
is the profile for the transport type beep.
- Cooked—sets the syslog profile as Cooked.
- Syslog FileName One—enter the first file
where the syslog can store the messages locally in three different
files. This scalar is to get the file name. This is a string with maximum
size of 32.
- Syslog FileName Two—enter the first file
where the syslog can store the messages locally in three different
files. This scalar is to get the file name. This is a string with
maximum size of 32.
- Syslog FileName Three—enter the first
file where the syslog can store the messages locally in three different
files. This scalar is to get the file name. This is a string with
maximum size of 32.
- Syslog Relay Port—enter the syslog port
on which the relay listens irrespective of the transport type. The
relay opens the socket and listens on the configured port. This
value ranges from 0 to 65535. The default value is 514.
- Syslog Snmp Trap—select the status for
generating Syslog server up/ down traps when connectivity fails.
The default option is Enabled. The list contains:
- Enabled—enables
the Syslog SNMP Traps. This generates
trap whenever connectivity to the external server collecting logs
is lost.
- Disabled—disables the Syslog SNMP Traps.
This does not generate Syslog SNMP server
up or down traps
- Syslog Relay Transport Type—select the
transport type to be used to send syslog messages. The default option
is UDP. The list contains:
- UDP—sets
the relay transport type as UDP i.e.
receiving syslog messages through UDP socket. TCP—sets the relay transport type
as TCP i.e. receiving syslog messages
through TCP socket.
|
| Fields (cont) |
- Syslog Authentication Type—select
the authentication mode to be used for sending email alerts to the
mail server configured. The default option is No Authentication.
The list contains:
- No Authentication—sets the SMTP authentication mode as No
Authentication, where email alerts are sent without authentication.
- AUTH LOGIN—sets the SMTP authentication
mode as AUTH LOGIN in which both the user name and password are
BASE64 encoded—email alerts are sent after authenticating the user
- AUTH PLAIN—sets the authentication mode as AUTH PLAIN in which
the authentication is done by sending the BASE64 encoded username
and password in a single statement—email alerts are sent after authenticating
the user.
- CRAM MD5—sends the BASE64 encoded user name and 16-byte digest
in hexadecimal notation. The digest is generated using HMAC calculation
with password as secret key and SMTP server
original challenge as the message—E-mail alerts are sent after authenticating
the user.
- DIGEST MD5—sets the SMTP authentication
method as DIGEST-MD5 in which the BASE64 encoded MD5 digest response
string that is calculated using the user name, password, realm string
and nonce string, and where email alerts are sent after authenticating
the user.
|
| Buttons |
- Reset—resets
to default value for respective fields and discards all user inputs.
- Apply—modifies attributes and saves the
changes
|
Figure 3. BSD
Logging Settings
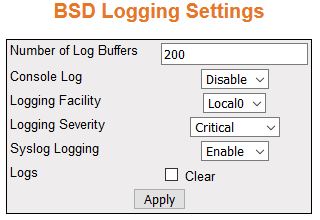
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user configure the BSD
Logging. This screen lists several parameters, such as logging
severity. All parameters are related to the configuration of logging
mechanism of Syslog and email alert messages in the local system.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Number of Log Buffers—enter
the number of logs and email alert messages that can be stored in
a local buffer for the syslog messages. This value ranges from 1
to 200. The default value is 50.
- Console Log—select the option to set
the status of console log. This enables or disables the logs and
email alert messages to be displayed in the console while being
sent to the server. The default option is Enable. The list contains:
- Enable—enables the console Log option. This sends the log and
email alert messages to the server and it will be displayed in the
console as well.
- Disable—disables the console log option. This sends the log
and email alert messages to the server alone and it will not be
displayed in the console.
- Logging Facility—select the facility
level used for storing the logs and email alert messages. The facility
refers to different general classification of the messages. The
default option is Local0. The list contains:
- Local0—specifies
that it is reserved for local use facility
- Local1—specifies that it is reserved for local use facility
- Local2—specifies that it is reserved for local use facility
- Local3—specifies that it is reserved for local use facility
- Local4—specifies that it is reserved for local use facility
- Local5—specifies that it is reserved for local use facility
- Local6—specifies that it is reserved for local use facility
- Local7—specifies that it is reserved for local use facility
- Logging Severity—select the facility
level used for storing the logs and email alert messages. The facility
refers to different general classification of the messages. The
default option is Local0. The list contains:
- Emergency—sets
the severity level as emergency where the messages can be logged
during panic condition.
- Alert—sets the severity level as alert where the messages require
immediate attention.
- Critical—sets the severity level as critical where the messages
represent critical error.
- Error—sets the severity level as error where t error messages
can be logged.
- Warning—sets the severity level as warning i.e. warning messages
can be logged.
- Notice—sets the severity level as notice or where the log messages
represent significant condition but not errors.
- Info—sets the severity level as info or where informational
messages can be logged.
- Debug—sets the severity level as debug or where the debug messages
can be logged.
|
| Fields (cont) |
|
| Buttons |
- Apply—modifies
attributes and saves the changes
|
BSD Syslog File Table
Figure 4. BSD Syslog File Table

| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user configure the BSD
syslog file table settings. |
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- File Priority—enter
the priority for which the log messages should be written in file.
This value ranges from 0 to 191, where 0 is considered the lowest
priority and 191 is the highest priority.
- File Name—enter the file name in which
the syslog message should be written.
Note: The file name should
be one of the file names configured in BSD Syslog Setting screen.
|
| Buttons |
- Add—adds and
saves a new configuration.
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|
BSD Syslog Mail Table
Figure 5. BSD Syslog Mail Table
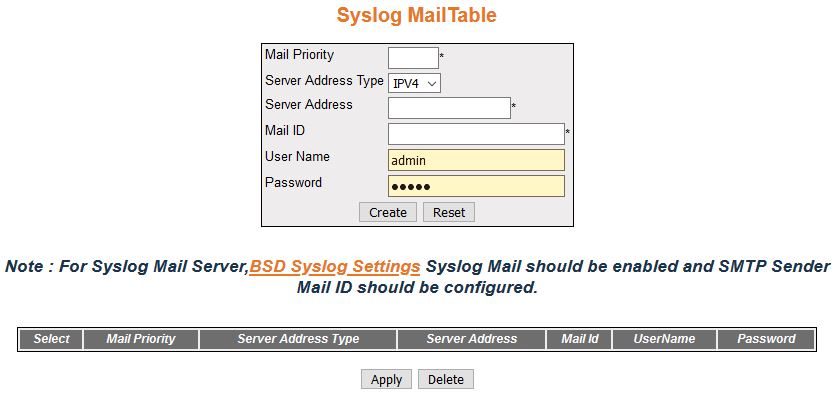
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user configure the BSD syslog mail table settings. |
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
|
| Buttons |
- Create—adds
and saves a new configuration.
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs.
- Apply—modifies attributes for the selected
entry and saves the changes.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|
BSD Syslog Forward Table
Figure 6. BSD Syslog Forward Table
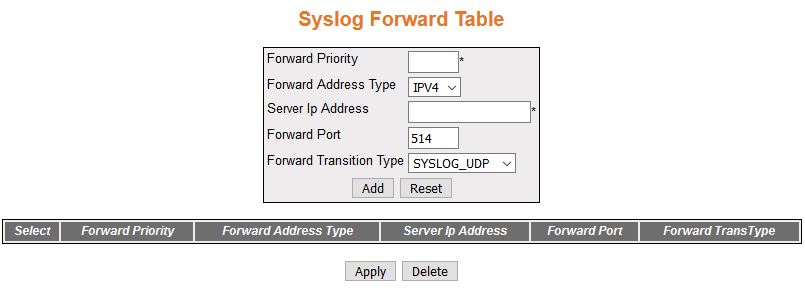
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user configure the BSD Syslog Forward table settings. |
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Forward Priority—enter
the priority at which the syslog messages are to be forwarded to
the desired server. This value ranges from 0 to 191.0 is considered as
the lowest priority and 191 is the highest priority.
- Forward Address Type—select the address
type for the server at which the syslog messages need to be forwarded. IPv4 stands for Server Address
Type of Internet Protocol Version 4.
- Server IP Address—enter the server IP
to which the syslog messages are to be forwarded.
- Forward Port—enter the port through which
the syslog message can be forwarded. This value ranges from 0 to
65535. The default value is 514.
- Forward Transition Type—select the transport
type by which the syslog message can be forwarded. The default option
is SYSLOG_UDP. The list contains:
- SYSLOG_UDP—sets the forward
transition type as SYSLOG_UDP
- SYSLOG_TCP—sets the forward transition type as SYSLOG_TCP
|
| Buttons |
- Create—adds
and saves a new configuration.
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs.
- Apply—modifies attributes for the selected
entry and saves the changes.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|