Describes the QoS Egress
settings.
QoS Egress refers
to the quality of service offered to the outgoing packets.
To access QoS Egress screens, go to .
Queue Template Settings
By
default, the tab QoS Egress displays the Queue
Template Settings screen.
Figure 1. Queue Template
Settings
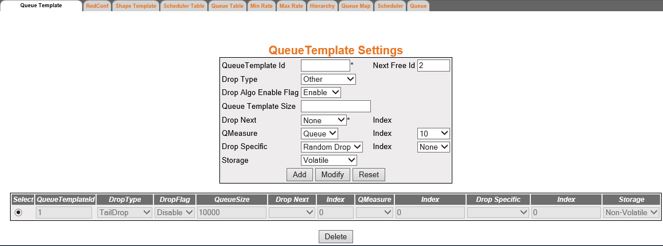
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to configure the
queue template settings. The QueueTemplate table is a template for
specifying the queue parameters and the policing algorithm parameters
applied on the queue. The template is re-used for configuring multiple
queues. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- QueueTemplate Id—enter
the index that enumerates the queue entries. This value ranges from
1 to 65535.
Note: The default Queue Template with an Id of 1 is
already created in the system and cannot be deleted.
- Next Free Id—specifies an integer which
may be used as a new index in the table. The value of zero indicates
that no more new entries can be created in the relevant table. This
is a read only field.
- Drop Type—select the type of drop algorithm
used by this queue template. The default option is TailDrop. Options
are:
- Other—sets the drop algorithm type as other.
- TailDrop—sets the drop type as Tail Drop. In this algorithm
the Queue Template size represents the maximum depth of the queue,
beyond which all newly arriving packets are dropped.
- HeadDrop—sets the drop type as Head Drop. This algorithm drops
the packets currently at the head of the queue to make room for
the new packet to be enqueued at the tail of the queue if a packet
arrives, when the current depth of the queue is at queue template
size.
- RED—sets the drop type as RED. This executes an active queue management
algorithm which may randomly drop a packet on packet arrival. This
algorithm may be proprietary, and it may drop either the arriving
packet or another packet in the queue.
- AlwaysDrop—sets the drop type as AlwaysDrop. This algorithm
implies that the packets are always dropped.
- WRED—sets the drop type as WRED (Weighted Random Early Detection). WRED is an enhanced RED mechanism for congestion avoidance with
support for six drop profiles maintained separately for each color (green,
yellow, and red) TCP or NON-TCP traffic. On packet arrival,
an Active Queue Management algorithm is executed which may randomly drop
a packet.
|
| Fields |
- Drop Algo Enable Flag—select
the option for enabling /disabling drop algorithm for congestion
management. The default option is Enable. Options are:
- Enable—enables
drop algorithm for congestion management.
- Disable—disables drop algorithm for congestion management.
- Queue template size—enter the queue size.
This is depth in bytes of the queue being measured, at which a trigger
is generated to the dropping algorithm. This value ranges from 0
to 65535.The default value is 10000.
Note: The value of this field
must be greater than or equal to the Random Detect Min Average Threshold
and less-than/equal to Random Detect Max Average Threshold if Random
Detection is enabled. The threshold value can be configured using
the RedConf Settings screen.
Note: For the tailDrop
or headDrop algorithms, this field represents the depth of the queue
at which the drop action will take place
- Drop Next—selects the next differentiated
services functional data path element to handle traffic for this
data path. The default option is None. Options are:
- None—disables
the drop next option.
- Classifier—sets classifier as the next differentiated services
functional data path element to handle traffic for this data path.
- Meter—sets meter as the next differentiated services functional
data path element to handle traffic for this data path.
- Action—sets Action as the next differentiated services functional
data path element to handle traffic for this data path.
- Queue—sets Queue as the next differentiated services functional
data path element to handle traffic for this data path
- Index—select the available entries of
corresponding functional blocks displayed by Drop Next.
- QMeasure—select the Qmeasure to indicate
the queue that a drop algorithm is to monitor when deciding whether
to drop a packet. If the row pointed to does not exist, the algorithmic
dropper element is considered inactive
- Index—select the available entries of
corresponding functional blocks displayed by QMeasure.
- Drop Specific—select the drop specific
entry that provides further detail regarding a drop algorithm. Options
are:
- Random Drop—enables random points to a table entry that
provides further detail regarding a drop algorithm.
- Index—select the available entries of
corresponding functional blocks displayed by Drop Specific.
|
| Fields (cont) |
- Storage—select
the storage type for the conceptual row. The default option is Non-Volative.
Options are:
- Volatile—reflects the configurations for an
interface whose interface index has been assigned, and for which
the supporting implementation is currently present.
- Non-Volatile—reflects the configuration for an interface whose
interface index has been assigned, but for which the supporting
implementation is currently not present.
|
| Buttons |
- Add—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Modify—modifies attributes and saves
the changes.
Note: The attributes of the default Queue Template
cannot be modified
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs.The attributes of the default
Queue Template cannot be modified.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
Note: The
default Queue Template Id 1 cannot be deleted.
|
Red Conf Settings
Figure 2. Red
Conf Settings—Part A
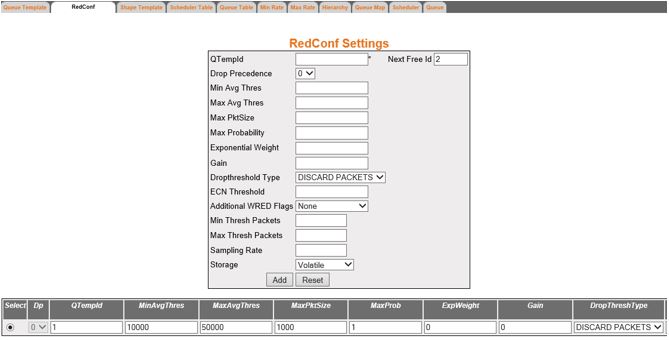
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to configure parameters
for Random Detect Algorithm. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- QTempId—enter
the index that enumerates the queue entries. This value ranges from
0 to 65535.
- Next Free Id—specifies an integer which
may be used as a new index in the table. The value of zero indicates
that no more new entries can be created in the relevant table. This
is a read-only field.
- Drop Precedence—select the drop precedence.
The default option is 0. The list contains:
- 0—sets low drop
precedence—discards TCP Green.
- 1—sets medium drop precedence—discards TCP Yellow.
- 2—sets high drop precedence—discards TCP Red.
- 3—discards NON-TCP Green
- 4—discards NON-TCP Yellow
- 5—Discards NON-TCP Red
- Max Avg Thres—enter the maximum average
threshold for the random detect algorithm. Below this threshold,
packets are admitted into the queue. This value ranges from 0 to
65535.The default value is 50000.
Note: The value of this field
should be greater than or equal to the Min Avg Threshold and less
than or equal to the Queue Size. The Queue Size can be configured
using the Queue Template Settings screen.
Note: The
units for this is based on the Drop Threshold Type configured.
- Min Avg Thres—enter the minimum average
threshold for the random detect algorithm. Below this threshold,
packets are admitted into the queue. This value ranges from 0 to
65535.The default value is 10000.
Note: The value of this field
should be less than or equal to the Max Avg Threshold and the Queue
Size. The Queue size can be configured using the Queue Template
Settings screen.
Note: The units for this is based
on the Drop Threshold Type configured.
- Max PktSize—enter the maximum allowed
packet size. This value ranges from 0 to 65535 bytes. The default
value is 1000.
- Max Probability—enter the percentage
of maximum probability of discarding a packet. This value ranges
from 1 to 100. The default value is 100.
- Exponential Weight—enter the exponential
weight for determining the average queue size. This value ranges
from 0 to 31. The default value is 0.
- Gain—enter the gain value which defines
an increase in drop-probability on each granular increase of buffer-occupancy
due to received traffic. This determines the smoothing that should
be applied. The value ranges from 0 to 100. The default value is
0.
|
| Fields (cont). |
- Dropthreshold Type—select
the drop threshold type to set the WRED drop type.
The default option is DISCARD PACKETS. The list contains:
- DISCARD
PACKETS—sets the WRED drop
type to Discard packets.
- DISCARD BYTES—sets the WRED drop type to Discard in terms
of bytes.
Note: Value configured for Min Avg Thresh and Max Avg
Thresh is interpreted as Packets/Bytes based on the selected option
- ECN Threshold—enter the Explicit Congestion
Notification (ECN) threshold to
define the Queue depth in bytes to stop marking and start dropping ECN eligible packets. The value
ranges from 0 to 65535. The default value is 0.
- Additional WRED Flags—select the option
to define the additional flags type for the WRED profiles. The default
option is None. The list contains:
- None—disables the additional WRED flags option.
- CapAverage—sets the average queue size as always less than the actual
queue size.
- MarkCongestion—marks ECN instead
of dropping the WRED profiles.
- Both—selects both CapAverage and MarkCongestion options to define the
additional flags type for the WRED profiles.
- Min Thresh Packets—specifies the average
queue depth in packets, beyond which traffic has a non-zero probability
of being dropped. This value ranges from 1 to 4294967295. This is
read only field.
- Max Thresh Packets—specifies the average
queue depth beyond which traffic has a probability indicated by
Max Probability of being dropped or marked. This value ranges from
1 to 4294967295.This is read only field.
- Sampling Rate—enter the number of times
per second the queue is sampled for queue average calculation. A
value of zero is used to mean that the queue is sampled approximately
each time a packet is enqueued (or dequeued). This value ranges
from 1 to 1000000. Default value is 0.
- Storage—select the storage type for the
conceptual row. The default option is Non-Volative.
Options are:
- Volatile—reflects the configurations for an
interface whose interface index has been assigned, and for which
the supporting implementation is currently present.
- Non-Volatile—reflects the configuration for an interface whose
interface index has been assigned, but for which the supporting
implementation is currently not present.
|
| Buttons |
- Add—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Modify—modifies attributes and saves
the changes.
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs.The attributes of the default
Queue Template cannot be modified.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
Note: The
entries can be deleted only if the Drop Algorithm Flag for the queue
template is disabled using the Queue Template Settings screen.
|
Scheduler Table Settings
Figure 3. Scheduler Table Settings
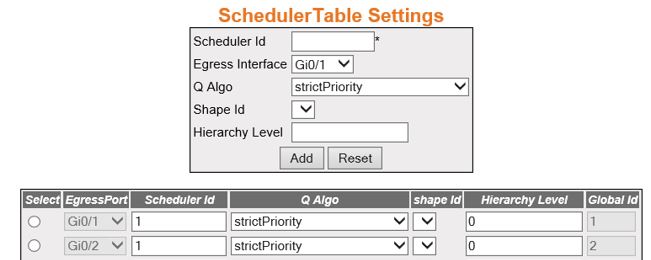
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to choose the Scheduler
settings. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
- The entries in the bottom form are displayed only if QoS is started in the system.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Scheduler Id—enter
the scheduler identifier that uniquely identifies the scheduler
in the system/egress interface. This value ranges from 0 to 65535.
- Egress Interface—select the outgoing
port number which is already specified in the system.
- Q Algo—select the option to set the packet
scheduling algorithm for the port. The default option is strictPriority.
Options are:
- strictPriority—enables the strict priority algorithm
for the port.
- roundRobin—enables round robin algorithm for the port.
- weightedRoundRobin—enables weighted round robin algorithm for the
port.
- Shape Id—select the shaper identifier
that specifies the bandwidth requirements for the scheduler. This
value ranges from 0 to 65535.
Note: This field list the shape
IDs configured using the Shape Template Settings scree.
- Hierarchy Level—enter the depth of the
queue/scheduler hierarchy. This value ranges from 0 to 10. A value
of 0 indicates that there is no hierarchy and that all queues/schedulers
are port-bound. The default value is 0.
- Global Id—specifies the scheduler identifier
that uniquely identifies the scheduler in the system / egress interface.
This value ranges from 0 to 65535.
|
| Buttons |
|
Queue Table Settings
Figure 4. Queue Table Settings
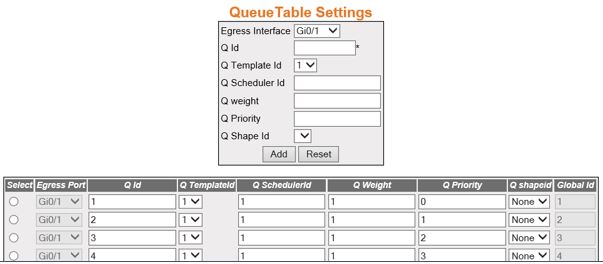
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to choose the queue
table settings. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
- The entries in the bottom form are displayed only if QoS is started in the system.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Egress Interface—select
the outgoing port number from the list of interfaces created in
the system.
- Q Id—enter the queue identifier that
uniquely identifies the queue in the system/port. This value ranges
from 1 to 65535.
- Q Template Id—select the queue template
ID applied for configuring queue attributes. This value ranges from
1 to 65535.
Note: This field lists the queue template id created
using the Queue Template Settings screen.
- Q Scheduler Id—enter the scheduler identifier
that manages the specified queue. This identifier is unique relative
to an egress interface. This value ranges from 1 to 65535.
- Q weight—enter the user assigned weight
to the CoS queue. The assigned weights
are used only when the scheduling algorithm is a weighted scheduling
algorithm. This value ranges from 1 to 1000. The default value is
0.
|
| Fields (cont) |
- Q Priority—enter
the user assigned priority for the CoS queue.
The assigned priority is used only when the scheduler uses a priority
based scheduling algorithm. This value ranges from 0 to 15. The
default value is 0.
- Q Shape Id—select the shaper identifier
that specifies the bandwidth requirements for the queue. The default
value is None.
|
| Buttons |
- Add—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Modify—modifies attributes and saves
the changes.
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs. The attributes of the default
Queue Template cannot be modified.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|
Min Rate
Figure 5. Min Rate
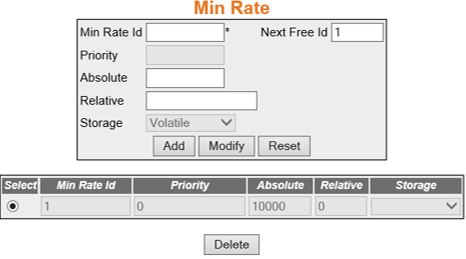
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to configure the
minimum rate settings. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
- The entries in the bottom form are displayed only if QoS is started in the system.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Min Rate Id—enter
the index that enumerates the minimum rate parameter entries. This
value ranges from 1 to 65535.
- Next Free Id—specifies an integer which
may be used as a new index in the table. The value of zero indicates
that no more new entries can be created in the relevant table. This
is a read-only field.
- Priority—this field is greyed out.
|
| Fields (cont) |
- Absolute—enter
the minimum absolute rate, in kilobits/sec, that a downstream scheduler
element should allocate to this queue. If the value is zero, then
there is effectively no minimum rate guarantee. If the value is
non-zero, the scheduler will assure the servicing of this queue
to at least this rate. This value ranges from 1 to 4294967295. The
default value is 10000.
- Relative—enter the minimum rate that
a downstream scheduler element should allocate to this queue, relative
to the maximum rate of the interface as reported by ifSpeed or ifHighSpeed,
in units of 1/1000 of 1. If the value is zero, then there is effectively
no minimum rate guarantee. If the value is non-zero, the scheduler
will assure the servicing of this queue to at least this rate. This
value ranges from 1 to 4294967295.
- Storage—select the storage type for the
conceptual row. The default option is Non-Volative.
Options are:
- Volatile—reflects the configurations for an
interface whose interface index has been assigned, and for which
the supporting implementation is currently present.
- Non-Volatile—reflects the configuration for an interface whose
interface index has been assigned, but for which the supporting
implementation is currently not present.
|
| Buttons |
|
Max Rate
Figure 6. Max Rate

| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to configure the
minimum rate settings. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
- The entries in the bottom form are displayed only if QoS is started in the system.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Max Rate Id—enter
the index that enumerates the minimum rate parameter entries. This
value ranges from 1 to 65535.
Note: The Max rate entries with
IDs 1 and 2 are already created in the system and cannot be deleted.
- Next Free Id—specifies an integer which
may be used as a new index in the table. The value of zero indicates
that no more new entries can be created in the relevant table. This
is a read-only field.
- Absolute—enter the maximum absolute rate,
in kilobits/sec, that a downstream scheduler element should allocate
to this queue. If the value is zero, then there is effectively no
maximum rate limit, and the scheduler should attempt to work conserving
for this queue. If the value is non-zero, the scheduler will limit
the servicing of this queue to, at most, this rate in a non-work-conserving
manner. This value ranges from 1 to 4294967295.
|
| Fields (cont) |
- Relative—enter
the maximum rate that a downstream scheduler element should allocate
to this queue, relative to the maximum rate of the interface as
reported by ifSpeed or ifHighSpeed, in units of 1/1000 of 1. If
the value is zero, then there is effectively no maximum rate limit
and the scheduler should attempt to work conserving for this queue.
If the value is non-zero, the scheduler will limit the servicing
of this queue to, at most, this rate in a non-work-conserving manner.
This value ranges from 1 to 4294967295.
- Threshold—specifies the number of bytes
of queue depth at which the rate of a multi-rate scheduler will
increase to the next output rate. In the last conceptual row for
such a shaper, this threshold is ignored and by convention is zero.
This value ranges from 1 to 4294967295.
- Storage—select the storage type for the
conceptual row. The default option is Non-Volative.
Options are:
- Volatile—reflects the configurations for an
interface whose interface index has been assigned, and for which
the supporting implementation is currently present.
- Non-Volatile—reflects the configuration for an interface whose
interface index has been assigned, but for which the supporting
implementation is currently not present.
|
| Buttons |
|
Queue Map Settings
Figure 7. QueueMap
Settings
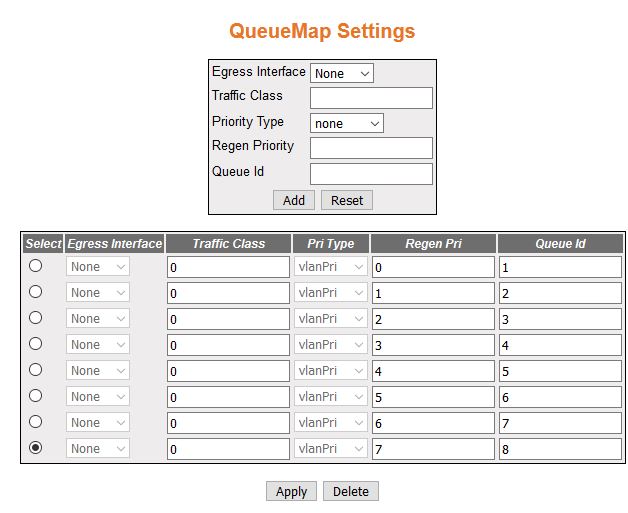
| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to map an egress
port, CLASS of service to a queue. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
- The entries in the bottom form are displayed only if QoS is started in the system.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Egress Interface—select
the outgoing port number from the list of interfaces created in
the system.
- Traffic Class—enter the input class (associated
with an incoming packet) that needs to be mapped to an outbound
queue. This value ranges from 1 to 65535.
|
| Fields (cont) |
- Priority Type—select
the regenerated-priority type to interpret the value of RegenPriority
object. Options are
- None—disables regenerated-priority type
to interpret the value of RegenPriority object.
- vlanPri—sets the regenerated-priority type to interpret the
value of RegenPriority object as Vlan.
- ipTos—sets the regenerated-priority type to interpret the value
of RegenPriority object as IP Type of Service type.
- ipDscp—sets the regenerated-priority type to interpret the value
of RegenPriority object as IP Differentiated Services Code Point.
- mplsExp—sets the regenerated-priority type to interpret the
value of RegenPriority object as MPLS Experimental.
- vlanDEI—sets the regenerated-priority type to interpret the
value of RegenPriority object as VLAN Drop Eligibility Indicator.
- Regen Priority—enter the regenerated-priority
(for an incoming packet) that needs to be mapped to an outbound
queue. This is mutually exclusive to the CLASS configuration. This
value ranges from 0 to 63.
- Queue Id—enter the queue identifier that
uniquely identifies a queue relative to an interface. It could be
configured with a unique value in the system. This value ranges
from 1 to 65535.
|
| Buttons |
- Add—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Modify—modifies attributes and saves
the changes.
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs.The attributes of the default
Queue Template cannot be modified.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|
Scheduler
Figure 8. Scheduler

| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to choose the Scheduler
settings. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
- The entries in the bottom form are displayed only if QoS is started in the system.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Scheduler Id—enter
the index that enumerates the scheduler entries. This value ranges
from 0 to 65535.
- Next Free Id—specifies an integer which
may be used as a new index in the table. The value of 0 indicates
that no more new entries can be created in the relevant table. This
is a read only field.
- Scheduler Next—select the next differentiated
services functional data path element to handle traffic for this
data path. Options are:
- None—disables traffic handling.
- Classifier—enables classifier setting.
- Meter—enables the meter setting.
- Action—enables the action setting.
- AlgoDrop—enables the algorithm drop setting
|
| Fields (cont) |
- Method—select
the scheduling algorithm used by this scheduler. Options are:
- Priority—enables
the priority scheduling algorithm.
- WRR—enables the weighted round robin scheduling algorithm.
- WFQ—enables the weighted fair queuing scheduling algorithm.
- Scheduler Min Rate—select the entry in
minimum rate table which indicates the priority or minimum output
rate from this scheduler. This attribute is used only when there
is more than one level of scheduler.
- Index—specifies the available entries
of corresponding functional blocks displayed by Scheduler Min Rate.
- Scheduler Max Rate—select the entry in
maximum rate table which indicates the maximum output rate from
this scheduler. When more than one maximum rate applies (for example,
when a multi-rate shaper is in view), it points to the first of
those rate entries. This attribute is used only when there is more
than one level of scheduler.
- Index—specifies the available entries
of corresponding functional blocks displayed by Scheduler Max Rate.
- Storage—select the storage type for the
conceptual row. The default option is Non-Volative.
Options are:
- Volatile—reflects the configurations for an
interface whose interface index has been assigned, and for which
the supporting implementation is currently present.
- Non-Volatile—reflects the configuration for an interface whose
interface index has been assigned, but for which the supporting
implementation is currently not present.
|
| Buttons |
- Add—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Modify—modifies attributes and saves
the changes.
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs.The attributes of the default
Queue Template cannot be modified.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|
Queue
Figure 9. Queue

| Screen Objective |
This screen allows the user to choose the queue
parameters. |
Note: - This screen can
be configured only if QoS is started
in the system using the Basic Settings screen.
|
| Navigation |
|
| Fields |
- Queue Id—enter
the index that enumerates the queue entries. This value ranges from
0 to 65535.
- Next Free Id—specifies an integer which
may be used as a new index in the table. The value of 0 indicates
that no more new entries can be created in the relevant table. This
is a read only field.
- Queue Next—select the next differentiated
services scheduler.
- Index—specifies the available entries
of corresponding functional blocks displayed by Queue Next.
|
| Fields (cont) |
- Queue Min Rate—select
the minimum rate entry that the scheduler, pointed to by Queue Next,
should use to service this queue.
- Index—specifies the available entries
of corresponding functional blocks displayed by Queue Min Rate.
- Queue Max Rate—select the maximum rate
entry that the scheduler, pointed to by Queue Next, should use to
service this queue.
- Index—specifies the available entries
of corresponding functional blocks displayed by Queue Max Rate.
- Storage—select the storage type for the
conceptual row. The default option is Non-Volative.
Options are:
- Volatile—reflects the configurations for an
interface whose interface index has been assigned, and for which
the supporting implementation is currently present.
- Non-Volatile—reflects the configuration for an interface whose
interface index has been assigned, but for which the supporting
implementation is currently not present.
|
| Buttons |
- Add—adds and
saves new configuration.
- Modify—modifies attributes and saves
the changes.
- Reset—resets to default value for respective
fields and discards all user inputs.The attributes of the default
Queue Template cannot be modified.
- Delete—deletes the selected entry.
|